chapter-4 栈
特点
- 高效的数据结构
- 数据只能在栈顶添加或删除
- 特殊的列表,栈内元素只能通过列表的一端访问,这一段称为栈顶。
- 后入先出(LIFO)的数据结构
- 任何不在栈顶的元素都无法访问,为了得到栈底的元素,必须先拿掉上面的元素
- 入栈(push),出栈(pop)、预览栈顶元素(peek)
栈的实现
|
|
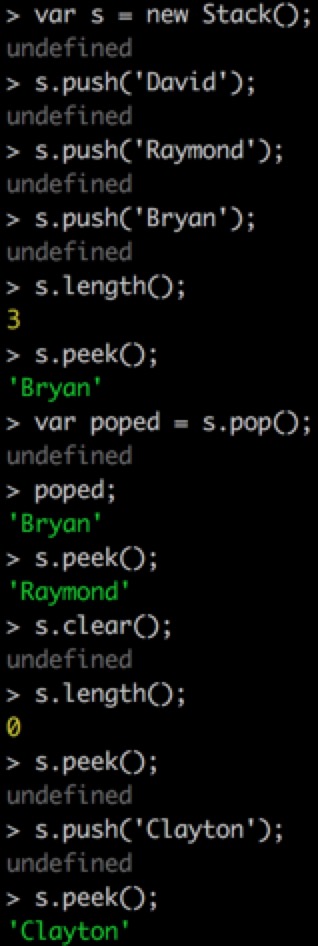
测试结果
实际问题
将数字n转换为以b为基数的数字,实现转换
- 最高位为n%b,压入栈
- 使用n/b代替n
- 重复前两步,知道n = 0,没有余数
- 弹出栈内元素,排列
只针对基数为2-9的情况(why?)
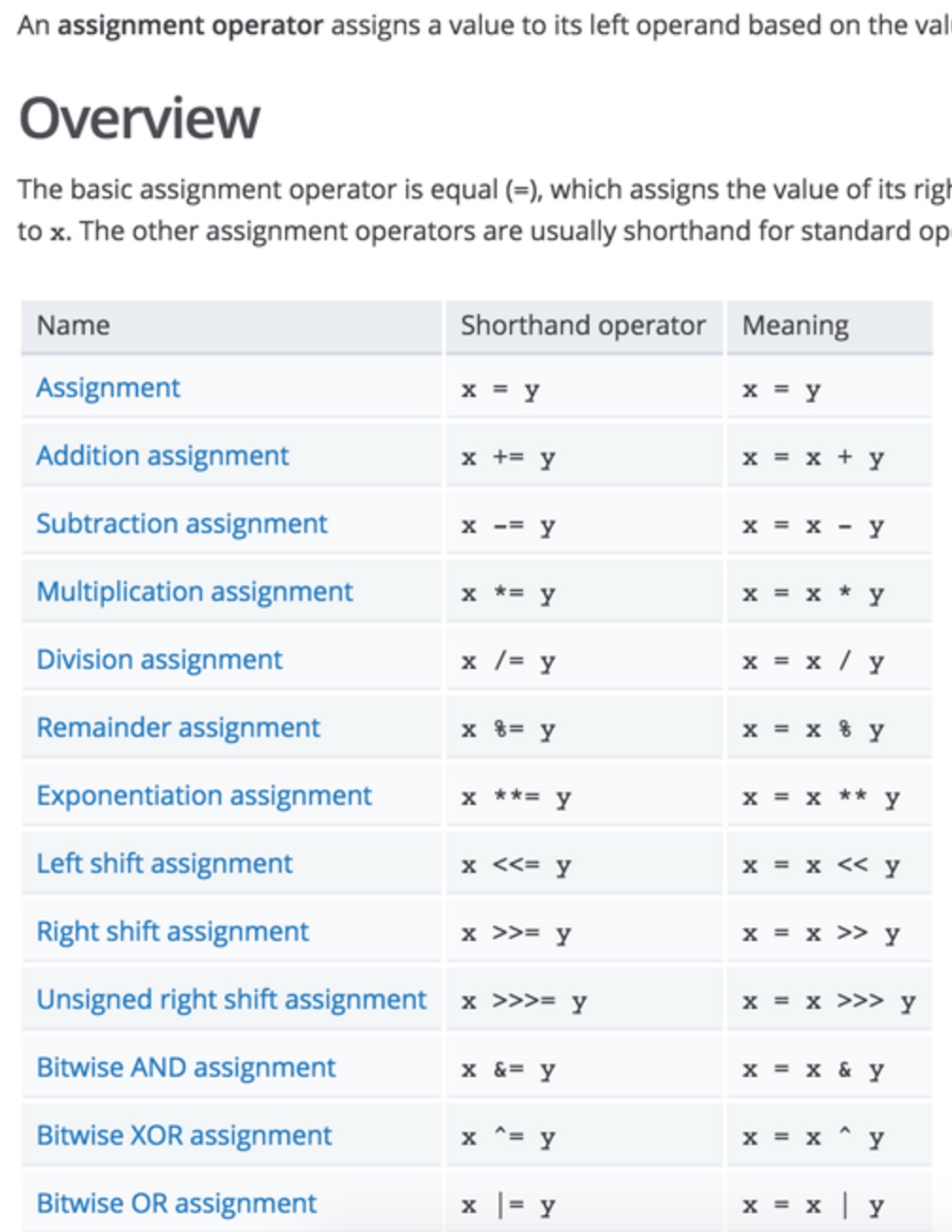
操作符的参考资料:https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaS
cript/Reference/Operators/Assignment_Operators
数制间转换
|
|
回文
- 一个单词、短语或数字,从前往后写和从后往前写都是一样的123456789101112131415161718function isPalindrome (word) {var s = new Stack();for (var i = 0; i < word.length;i++){s.push(word[i]);}var rword = '';while (s.length() > 0) {rword += s.pop();}if (word === rword) {return true;} else {return false;}console.log(s.dataStore)}isPalindrome('hello');// falseisPalindrome('racecar');// true
递归演示
- 模拟递归过程12345678910111213141516171819202122// 使用栈模拟递归过程function factorial (n) {if (n === 0) {return 1;} else {return n * factorial(n - 1);}}function fact (n) {var s = new Stack();while (n > 1) {s.push(n--);}var product = 1;while (s.length() > 0) {product *= s.pop();}return product;}factorial(5);// 120fact(5);// 120